The diabetes mellitus - A disorder that develops when the cells of the body do not receive enough insulin. This hormone is produced by the pancreas; it normally enables body cells to take in glucose from the blood to generate energy, and enables the liver and fat cells to take in glucose for storage. A lack of insulin in the cells may occur because the pancreas produces too little, or none at all; alternatively, it may occur because the tissues are resistant to the hormone’s effects.
TYPES, CAUSES, AND INCIDENCE:
There are two main types of diabetes mellitus, both of which tend to run in families. Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes usually develops suddenly in childhood or adolescence. This type of diabetes is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system destroys insulin-secreting cells in the pancreas and insulin production ceases. Affected people may be genetically predisposed to developing the condition; the disease process may be triggered by viral infection. They must have insulin injections
or they may fall into a coma and die.
Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes tends to develop gradually, mainly in people over the age of 40. This type is becoming more common in younger people, however, and is probably linked to dieting. Although insulin is still produced, there is not enough to meet the body’s needs because the tissues become relatively resistant to its effects. Obesity and inheritance are possible contributory factors; many people whodevelop Type 2 diabetes are overweight, and affected people often have close relatives with the condition. Diabetes mellitus affects more than 120 million people worldwide. Type 2 diabetes is by far the more common form of the disease. About 1 in 50 people in the UK has this type. It is three to four times more common in black people, and seven times more common in Asians. It also becomes more common with increasing age.
SYMPTOMS:
Lack of insulin causes high levels of glucose to remain in the blood. This, in turn, results in a high level of glucose in the urine. This condition, termed glycosuria, causes the passage of large quantities of urine, excessive thirst, and urinary tract infections. Lack of glucose in the cells causes weight loss, hunger, and fatigue, and leads to chemical imbalances. For further information on the symptoms, see the illustrated box on the previous page.
In Type 1 diabetes, symptoms such as thirst, weight loss, and excessive urination usually develop rapidly over a few weeks. If it is not promptly diagnosed and treated at this stage, it may lead to diabetic ketoacidosis, which is a potentially fatal condition.
Type 2 diabetes may be present for months or years while causing few noticeable symptoms. It may only be diagnosed when a complication (see below), such as poor vision, is detected during a medical check-up.
COMPLICATIONS
Some complications of diabetes mellitus result from damage to capillaries (tiny blood vessels) throughout the body. These conditions include retinopathy (damage to the retina, which is the lightsensitive part of the eye) and diabetic nephropathy (kidney damage). Damage to the blood vessels supplying nerves causes diabetic neuropathy (damage to nerve fibres); this may first appear in the fingers and toes, then spread up the limbs.
The loss of sensation, and poor circulation, may result in ulcers on the feet and legs. Other problems include dizziness on standing and, in men, impotence. People with diabetes have a greater risk of developing atherosclerosis (accumulation of fatty deposits on the lining of the arteries), hypertension (high blood pressure), other cardiovascular disorders, and diabetic cataract (opacity in the lens of the eye).
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
If diabetes mellitus is suspected, a urine sample will be taken and tested for the presence of glucose. The diagnosis is confirmed by a blood test to detect abnormally high levels of glucose in the blood. If the results of this test are unclear, a glucose tolerance test may be done. The person is asked to fast for several hours, and then is given glucose; the blood and the urine are tested at 30-minute intervals to show how efficiently the body is utilizing the glucose. Tests may also be carried out to detect and assess damage to organs such as the eyes, kidneys, and heart.
Treatment aims to keep blood glucose levels as normal as possible. Dietary control is an essential element. The ideal diet for a person with diabetes resembles the sort of healthy eating plan recommended for everyone (see diabetic diet). If the person is overweight, and particularly if he or she has Type 2 diabetes, weight loss can be achieved by a reduced-calorie diet. Also, regular exercise and treatment with antidiabetic drugs may be required.
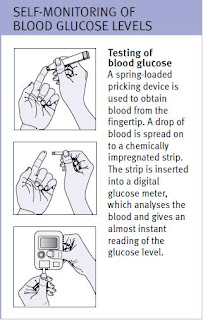
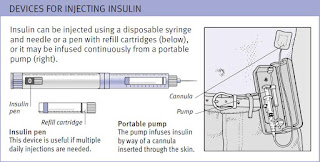
In addition to general treatment, all people with Type 1 diabetes need to have regular injections of insulin. The injections are usually self-administered two, three, or four times a day. The insulin doses need to be matched to activity levels and food intake. If the glucose/insulin balance is not maintained, hyperglycaemia (too much glucose in the blood) or hypoglycaemia (too little glucose in the blood) may develop. Careful monitoring of blood glucose levels is also an essential part of self-treatment. Pancreas transplants have been tried as a possible cure for the condition, but with little success. Research is being done on a possible treatment involving transplantation of clusters of insulin-producing cells.
Treatment of type 2 diabetes usually consists of dietary measures, weight reduction, exercise, and antidiabetic drugs, often hypoglycaemic drugs such as sulphonylureas. Some people eventually need insulin injections.
In general, careful control of blood glucose levels reduces the risk of complications or, if such problems have already developed, slow their progression. People with diabetes should have regular medical check-ups so that any complications can be detected as early as possible. Additional tests, such as measurement of glycosylated haemoglobin (which shows blood glucose levels over the previous three months) and urine tests to detect proteinuria, can improve medical control and aid early detection of problems.
OUTLOOK
With modern treatment and efficient self-monitoring, people with diabetes mellitus can usually live a normal life; however, the disease is irreversible and life expectancy is reduced.
Read More