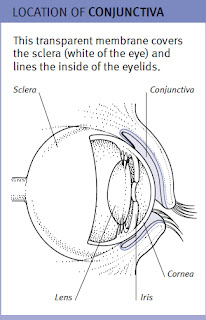
The conjunctiva - The transparent membrane covering the sclera (white of the eye) and lining the inside of the eyelids. Cells in the conjunctiva produce a fluid that lubricates the lids and the cornea.
9/10/15
conjunctiva
The conjunctiva - The transparent membrane covering the sclera (white of the eye) and lining the inside of the eyelids. Cells in the conjunctiva produce a fluid that lubricates the lids and the cornea.
congestion
The congestion - A term that usually refers to the accumulation of excess blood, tissue fluid, or lymph in part of the body.
A major cause of congestion is an increased blood flow to an area due to inflammation. Another possible cause is reduced drainage of blood from an affected area, as can occur in heart failure, in venous disorders such as varicose veins, and in lymphatic disorders. (See also nasal congestion.)
A major cause of congestion is an increased blood flow to an area due to inflammation. Another possible cause is reduced drainage of blood from an affected area, as can occur in heart failure, in venous disorders such as varicose veins, and in lymphatic disorders. (See also nasal congestion.)
- at 9:22 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
congenital
The congenital - A term meaning “present at birth”. Congenital abnormalities (sometimes called birth defects) may be inherited. Alternatively, they may result from damage or infection occurring either in the uterus or at the time of birth.
- at 8:53 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
confusion
The confusion - An acute or chronic disorganized mental state in which thought, memory, and reasoning are impaired.
CAUSES AND SYMPTOMS:
Acute confusion can arise as a symptom of delirium, in which brain activity is affected by fever, drugs, poisons, or injury. People with acute confusion may also have hallucinations and behave in a violent manner.
Chronic confusion is often associated with alcohol dependence, the long-term use of antianxiety drugs, and certain physically based mental disorders. Many of the conditions that cause chronic confusion (for example, dementia) are progressive. Features of such conditions include absentmindedness, poor short-term memory, and a tendency to be repetitive.
TREATMENT:
If the underlying cause of confusion can be treated, there may be marked improvement. Sedative drugs can be of benefit in acute confusion.
CAUSES AND SYMPTOMS:
Acute confusion can arise as a symptom of delirium, in which brain activity is affected by fever, drugs, poisons, or injury. People with acute confusion may also have hallucinations and behave in a violent manner.
Chronic confusion is often associated with alcohol dependence, the long-term use of antianxiety drugs, and certain physically based mental disorders. Many of the conditions that cause chronic confusion (for example, dementia) are progressive. Features of such conditions include absentmindedness, poor short-term memory, and a tendency to be repetitive.
TREATMENT:
If the underlying cause of confusion can be treated, there may be marked improvement. Sedative drugs can be of benefit in acute confusion.
- at 2:27 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
confluent
The confluent - A term meaning “merging or running together”. It is used, for example, in relation to individual skin blemishes that merge to form one abnormal area.
- at 2:25 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
confidentiality
The confidentiality - The ethical principle that a doctor does not disclose any information given in confidence by a patient.
The patient’s consent is necessary before a doctor supplies confidential information to an insurance company, an employer, or a lawyer. Doctors must, however, disclose information about patients when required to do so by law, or when they are faced with injuries or disorders that indicate a serious crime.
Doctors are also required to notify health authorities about patients with specified infectious diseases. Treatment of young children is usually discussed with the parents, but an older child’s request for confidentiality is generally respected if the doctor feels that he or she is competent enough to understand the issues involved.
The patient’s consent is necessary before a doctor supplies confidential information to an insurance company, an employer, or a lawyer. Doctors must, however, disclose information about patients when required to do so by law, or when they are faced with injuries or disorders that indicate a serious crime.
Doctors are also required to notify health authorities about patients with specified infectious diseases. Treatment of young children is usually discussed with the parents, but an older child’s request for confidentiality is generally respected if the doctor feels that he or she is competent enough to understand the issues involved.
- at 2:25 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
confabulation
The confabulation - The use of a fictional story to make up for gaps in memory. The phenomenon occurs most commonly in chronic alcoholics who suffer from Wernicke Korsakoff syndrome. It may also occur in people with head injuries.
- at 2:24 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
cone biopsy
The cone biopsy - A surgical procedure in which a conical or cylindrical section of tissue from the lower part of the cervix (neck of the uterus) is removed (see biopsy of the cervix box.
A cone biopsy is performed following an abnormal result of a cervical smear test if the extent of the precancerous or cancerous area cannot be seen by colposcopy (inspection of the cervix with a viewing instrument). (See also cervix, cancer of).
A cone biopsy is performed following an abnormal result of a cervical smear test if the extent of the precancerous or cancerous area cannot be seen by colposcopy (inspection of the cervix with a viewing instrument). (See also cervix, cancer of).
- at 2:20 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
cone
The cone - A type of light-sensitive cell located in the retina of the eye. Cones play a major role in colour vision.
- at 2:19 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
condyloma
The condyloma - A warty skin growth that usually occurring in moist areas of the body, for example the genitals. The most common type of condyloma is caused by the human papillomavirus (see genital warts).
Condylomata are highly infectious flattened growths that may develop around the genitals in the secondary stage of syphilis.
Condylomata are highly infectious flattened growths that may develop around the genitals in the secondary stage of syphilis.
- at 2:18 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
condyle
The condyle - A round projection on the end of a bone that fits into a hollow on another bone to form a joint; an example of a condyle is the elbow.
- at 2:17 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
conduit
The conduit - A channel or tube that conveys fluid. Conduits may be created surgically to redirect the flow of body fluids. The most common form of artificially constructed
conduit is an ileal conduit, which is created from part of the small intestine to divert urine out of the body when the bladder has had to be removed (see cystectomy).
conduit is an ileal conduit, which is created from part of the small intestine to divert urine out of the body when the bladder has had to be removed (see cystectomy).
- at 2:16 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
conductive deafness
The conductive deafness - Deafness caused by faulty conduction of sound from the outer to the inner ear. Causes include excess earwax or fluid in the middle ear (see glue ear).
- at 2:16 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
conduction
The conduction - The movement of particular forms of energy, such as nerve impulses and sound waves, through a system.
- at 2:14 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
conduct disorders
The conduct disorders - Repetitive and persistent patterns of aggressive and/or antisocial behaviour, such as vandalism, substance abuse, and persistent lying, in children or adolescents. (See also behavioural problems in children; adolescence.)
- at 2:14 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
condom, female
The condom, female - A barrier method of contraception in the form of a sheath that is inserted into a woman’s vagina before sexual intercourse. Female condoms also offer some protection against sexually transmitted infections.
- at 1:51 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
condom
The condom - A barrier method of contraception in the form of a thin latex rubber or plastic sheath, which is placed over a man’s penis before sexual intercourse. Condoms also provide some protection against sexually transmitted infections.
- at 1:51 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
conditioning
The conditioning - The formation of a specific physical or behavioural response to a particular stimulus in the environment.
CLASSICAL CONDITIONING:
In classical conditioning, a stimulus that consistently evokes a particular response is paired repeatedly with a second stimulus that would not normally produce the response. Eventually, the second stimulus begins to produce the response whether or not the first stimulus is present.
This phenomenon was shown by the physiologist Ivan Pavlov. He observed that dogs salivated in anticipation of food (an unconditioned response to a stimulus). He then devised a procedure in which a bell was rung every time a dog was given food; once the procedure had been repeated several times, the dog began to salivate every time it heard the bell (a conditioned response to a stimulus) even if no food was presented.
OPERANT CONDITIONING:
In operant conditioning, attempts are made to modify behaviour by rewarding or punishing a subject (animal or human) every time the subject shows a particular response to a specific stimulus. A response that is rewarded will be reinforced and become more frequent, while one that is punished will be inhibited and become less frequent.
USE IN MEDICINE:
Behavioural psychology (see behaviour therapy) is based on the idea that inappropriate behaviour patterns in some psychological disorders are learned through conditioning. It is thought that these patterns can be modified by the same process of conditioning.
CLASSICAL CONDITIONING:
In classical conditioning, a stimulus that consistently evokes a particular response is paired repeatedly with a second stimulus that would not normally produce the response. Eventually, the second stimulus begins to produce the response whether or not the first stimulus is present.
This phenomenon was shown by the physiologist Ivan Pavlov. He observed that dogs salivated in anticipation of food (an unconditioned response to a stimulus). He then devised a procedure in which a bell was rung every time a dog was given food; once the procedure had been repeated several times, the dog began to salivate every time it heard the bell (a conditioned response to a stimulus) even if no food was presented.
OPERANT CONDITIONING:
In operant conditioning, attempts are made to modify behaviour by rewarding or punishing a subject (animal or human) every time the subject shows a particular response to a specific stimulus. A response that is rewarded will be reinforced and become more frequent, while one that is punished will be inhibited and become less frequent.
USE IN MEDICINE:
Behavioural psychology (see behaviour therapy) is based on the idea that inappropriate behaviour patterns in some psychological disorders are learned through conditioning. It is thought that these patterns can be modified by the same process of conditioning.
- at 1:48 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
concussion
The concussion - Brief unconsciousness, usually following a violent blow to the head. The loss of consciousness is due to a brief disturbance of the electrical activity in the brain.
Common symptoms following concussion include confusion, inability to remember events that occurred just prior to the injury, dizziness, blurred vision, and vomiting. Anyone who has been concussed, however briefly, should see a doctor as soon as possible.
Persistent symptoms, or new ones such as drowsiness, difficulty in breathing, repeated vomiting, or visual disturbances, could signify brain damage or an extradural haemorrhage, and medical advice should be sought without delay. Repeated concussion can cause punch-drunk syndrome. (See also head injury.)
Common symptoms following concussion include confusion, inability to remember events that occurred just prior to the injury, dizziness, blurred vision, and vomiting. Anyone who has been concussed, however briefly, should see a doctor as soon as possible.
Persistent symptoms, or new ones such as drowsiness, difficulty in breathing, repeated vomiting, or visual disturbances, could signify brain damage or an extradural haemorrhage, and medical advice should be sought without delay. Repeated concussion can cause punch-drunk syndrome. (See also head injury.)
- at 1:46 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
conception
The conception - The fertilization of a woman’s ovum (egg) by a man’s sperm, followed by implantation of the resulting blastocyst (the growing mass of fertilized cells) in the lining of the uterus. This process marks the beginning of pregnancy. (See also contraception; infertility.)
- at 1:45 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
computer aided diagnosis
The computer aided diagnosis - The use of computer technology in certain diagnostic tests and procedures. It involves the use of probability-based computer systems that store information on thousands of cases of different disorders, detailing the type, location, duration, symptoms, medical history, and diagnosis.
A patient’s symptoms and medical history can be entered into a computer, which then compares the details with existing data and produces a list of the most likely diagnoses. Such technology is not currently in common use in hospitals, but is of value for people who are isolated from medical services, such as oil-rig crews.
Computers programmed to interpret visual data, such as abnormal cells, have potential use in certain types of blood test and cervical smear tests. Computers are also used in investigative procedures such as CT scanning and MRI.
A patient’s symptoms and medical history can be entered into a computer, which then compares the details with existing data and produces a list of the most likely diagnoses. Such technology is not currently in common use in hospitals, but is of value for people who are isolated from medical services, such as oil-rig crews.
Computers programmed to interpret visual data, such as abnormal cells, have potential use in certain types of blood test and cervical smear tests. Computers are also used in investigative procedures such as CT scanning and MRI.
- at 1:42 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
compression syndrome
The compression syndrome - A collection of localized neurological symptoms, such as numbness, tingling, discomfort, and muscle weakness, that is caused by pressure on a nerve.
- at 1:41 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
compress
The compress - A pad of lint or linen applied, under pressure, to an area of skin. Cold compresses soaked in ice-cold water or wrapped around ice help to reduce pain, swelling, and bleeding under the skin after an injury (see ice pack).
Hot compresses increase the circulation and help to bring boils to a head. A dry compress may be used to stop bleeding from a wound or may be coated with medication to help treat infection.
Hot compresses increase the circulation and help to bring boils to a head. A dry compress may be used to stop bleeding from a wound or may be coated with medication to help treat infection.
- at 1:40 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
compound fracture
The compound fracture - A type of fracture, also known as an open fracture, in which a broken bone breaks through the overlying skin. In this type of fracture, there is a high risk of infection.
- at 1:39 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
compound
The compound - A term used in chemistry to describe a substance that contains two or more chemically combined elements. In pharmacy, a compound is a preparation that contains a number of ingredients.
- at 1:38 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
complex
The complex - A term used in medicine to mean a group or combination of related signs and symptoms that form a syndrome (as in Eisenmenger complex), or a collection of substances of similar structure or function (as in vitamin B complex).
In psychology, a complex (for example, the Oedipus complex) denotes a group of unconscious ideas and memories that have emotional importance.
In psychology, a complex (for example, the Oedipus complex) denotes a group of unconscious ideas and memories that have emotional importance.
- at 1:37 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
complete abortion
The complete abortion - The expulsion from the uterus of an embryo or a fetus together with its membranes and placenta (see abortion).
- at 1:37 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
complementary medicine
The complementary medicine - A group of therapies, often described as “alternative”, that are now increasingly used to complement or to act as an alternative to conventional medicine.
Such treatments fall into three broad categories: touch and movement (as in acupuncture, massage, and reflexology); medicinal (as in naturopathy, Chinese medicine, and homeopathy); and psychological (as in biofeedback, hypnotherapy, and meditation).
Such treatments fall into three broad categories: touch and movement (as in acupuncture, massage, and reflexology); medicinal (as in naturopathy, Chinese medicine, and homeopathy); and psychological (as in biofeedback, hypnotherapy, and meditation).
- at 1:36 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
complement
The complement - A collection of proteins in the plasma (the fluid part of blood) that helps to destroy foreign cells and is an important part of the immune system.
- at 1:35 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
compensation
The compensation - The adjustment made by an organ to make up for changes in body function or structure. An example of compensation is the increased size of one kidney when the other has been removed.
- at 1:35 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
compartment syndrome
The compartment syndrome - A painful cramp due to compression of a group of muscles within a confined space. It may occur when muscles are enlarged due to intensive sports training or to an injury such as shin splints.
Cramps induced by exercise usually disappear when the exercise is stopped. Severe cases may require fasciotomy to improve blood flow and prevent development of a permanent contracture.
Cramps induced by exercise usually disappear when the exercise is stopped. Severe cases may require fasciotomy to improve blood flow and prevent development of a permanent contracture.
- at 1:34 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
communicable disease
The communicable disease - Any disease due to a microorganism or parasite that can be transmitted from one person to another. (See also contagious; infectious disease.)
- at 1:33 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
comminuted fracture
The comminuted fracture - A type of fracture in which the bone shatters into more than two pieces. A severe blow, such as an impact occurring in a car accident, may result in a comminuted fracture.
- at 1:32 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
commensal
The commensal - A bacterium or other organism that normally lives in or on the body without either harming or benefiting its host.
- at 1:32 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
coma
The coma - A state of unconsciousness and unresponsiveness to external stimuli (for example, pinching) or internal stimuli (such as a full bladder).
CAUSES:
Coma results from disturbance or damage to areas of the brain involved in conscious activity or maintenance of consciousness in particular, parts of the cerebrum, upper parts of the brainstem, and central regions of the brain, especially the limbic system.
Conditions that can produce coma include severe head injury; disorders such as stroke or cardiac arrest, in which part or all of the brain tissue is deprived of blood; or infectious disorders that affect the brain, such as meningitis and encephalitis. In addition, excessively high or low blood levels of certain substances may result in coma; for example, a person with diabetes mellitus may become comatose if his or her blood level of glucose (sugar) rises or falls to an abnormal degree.
SYMPTOMS:
There are varying depths of coma. In less severe forms, the affected person may make small movements and respond to certain stimuli. In a deep coma, the person does not make any movements or respond to any stimulus. However, even people in deep comas may show some automatic responses, for example breathing unaided and blinking. If the lower brainstem is damaged, however, vital functions are impaired, and artificial ventilation and maintenance of the circulation are required.
OUTLOOK:
If brain damage is minor and reversible, the person may make a full recovery, but deep coma due to severe trauma may result in long-term neurological problems such as muscle weakness or changes in behaviour. A person in a deep coma (a persistent vegetative state) may be kept alive for years provided the brainstem is still functioning. Complete and irreversible loss of brainstem function leads to brain death (the permanent cessation of all brain functions).
CAUSES:
Coma results from disturbance or damage to areas of the brain involved in conscious activity or maintenance of consciousness in particular, parts of the cerebrum, upper parts of the brainstem, and central regions of the brain, especially the limbic system.
Conditions that can produce coma include severe head injury; disorders such as stroke or cardiac arrest, in which part or all of the brain tissue is deprived of blood; or infectious disorders that affect the brain, such as meningitis and encephalitis. In addition, excessively high or low blood levels of certain substances may result in coma; for example, a person with diabetes mellitus may become comatose if his or her blood level of glucose (sugar) rises or falls to an abnormal degree.
SYMPTOMS:
There are varying depths of coma. In less severe forms, the affected person may make small movements and respond to certain stimuli. In a deep coma, the person does not make any movements or respond to any stimulus. However, even people in deep comas may show some automatic responses, for example breathing unaided and blinking. If the lower brainstem is damaged, however, vital functions are impaired, and artificial ventilation and maintenance of the circulation are required.
OUTLOOK:
If brain damage is minor and reversible, the person may make a full recovery, but deep coma due to severe trauma may result in long-term neurological problems such as muscle weakness or changes in behaviour. A person in a deep coma (a persistent vegetative state) may be kept alive for years provided the brainstem is still functioning. Complete and irreversible loss of brainstem function leads to brain death (the permanent cessation of all brain functions).
- at 1:26 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
colposcopy
The colposcopy - Viewing of the cervix (the neck of the uterus) and vagina using a magnifying instrument called a colposcope. Colposcopy is carried out to detect areas of precancerous tissue (see dysplasia) or of early cervical cancer (see cervix, cancer of).
Removal of tissue samples (see biopsy) or treatment to remove any abnormal areas can be performed during colposcopy, and this is usually done under local anaesthetic.
Removal of tissue samples (see biopsy) or treatment to remove any abnormal areas can be performed during colposcopy, and this is usually done under local anaesthetic.
- at 1:22 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
Colpermin
The Colpermin - A brand name for peppermint oil. This preparation is used to relieve the pain that results from muscle spasms in irritable bowel syndrome and diverticular disease.
- at 1:19 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
colour vision deficiency
The colour vision deficiency - Any abnormality in colour vision that causes a person to have difficulty in distinguishing between certain colours.
TYPES:
The most common type of colour vision deficiency is the reduced ability to discriminate between red and green. Most cases of red–green colour vision deficiency are the result of defects in the light-sensitive cells in the retina. These defects are usually inherited, and tend to be sex-linked (see genetic disorders); the majority of sufferers are male, while females are unaffected, but they can pass on the disorder to their children.
Occasionally, defects may be acquired as a result of diseases of the retina or the optic nerve, or they are caused by injury. There are two forms of red–green deficiency. A person with a severe green deficiency has difficulty in distinguishing between oranges, greens, browns, and pale reds. A severe red deficiency causes all shades of red to appear dull.
A much rarer colour vision deficiency exists in which blue cannot be distinguished. This condition may be inherited, or it may be due to degeneration of the retina or the optic nerve. Monochromatism (the total absence of colour vision) also exists, but this deficiency is very rare.
TYPES:
The most common type of colour vision deficiency is the reduced ability to discriminate between red and green. Most cases of red–green colour vision deficiency are the result of defects in the light-sensitive cells in the retina. These defects are usually inherited, and tend to be sex-linked (see genetic disorders); the majority of sufferers are male, while females are unaffected, but they can pass on the disorder to their children.
Occasionally, defects may be acquired as a result of diseases of the retina or the optic nerve, or they are caused by injury. There are two forms of red–green deficiency. A person with a severe green deficiency has difficulty in distinguishing between oranges, greens, browns, and pale reds. A severe red deficiency causes all shades of red to appear dull.
A much rarer colour vision deficiency exists in which blue cannot be distinguished. This condition may be inherited, or it may be due to degeneration of the retina or the optic nerve. Monochromatism (the total absence of colour vision) also exists, but this deficiency is very rare.
- at 1:18 AM
- Posted by Nursing Board Exam
- Categories C, Medical Term
- 0 comments
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)