9/25/15
cranial nerves
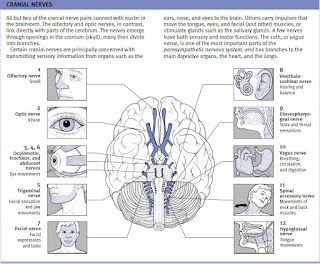
The cranial nerves - Twelve pairs of nerves that emerge from the underside of the brain. Each of the cranial nerves has a number as well as a name; the numbers are used to indicate the sequence in which the nerves emerge from the brain.
Certain cranial nerves primarily send sensory information from the ears, nose, and eyes to the brain. These nerves are the vestibulocochlear nerve (hearing and balance), olfactory nerve (smell), and optic nerve (vision). Other cranial nerves carry impulses that move the muscles in the head and neck. They are the oculomotor nerve, the trochlear nerve, and the abducent nerve (producing eye movements), the spinal accessory nerve (producing head and shoulder movements), and hypoglossal nerve (producing tongue movements).
Some cranial nerves have both sensory and motor functions. They are the facial nerve (facial expressions, taste, and the secretion of saliva and tears), the trigeminal nerve (facial sensation and jaw movements), and the glossopharyngeal nerve (taste and swallowing). The vagus nerve has branches to all the main digestive organs, as well as to the heart and the lungs. It is a major component of the parasympathetic nervous system, which is concerned with maintaining automatic body functions such as breathing, the heartbeat, and digestion.
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)




0 comments:
Post a Comment